A long-sought goal of creating particles that can emit a colorful fluorescent glow in a biological environment, and that could be precisely manipulated into position within living cells, has been achieved by a team of researchers at MIT and several other institutions. The finding is reported this week in the journal Nature Communications.
The new technology could make it possible to track the position of the nanoparticles as they move within the body or inside a cell. At the same time, the nanoparticles could be manipulated precisely by applying a magnetic field to pull them along. And finally, the particles could have a coating of a bioreactive substance that could seek out and bind with particular molecules within the body, such as markers for tumor cells or other disease agents.
“It’s been a dream of mine for many years to have a nanomaterial that incorporates both fluorescence and magnetism in a single compact object,” says Moungi Bawendi, the Lester Wolfe Professor of Chemistry at MIT and senior author of the new paper. While other groups have achieved some combination of these two properties, Bawendi says that he “was never very satisfied” with results previously achieved by his own team or others.
For one thing, he says, such particles have been too large to make practical probes of living tissue: “They’ve tended to have a lot of wasted volume,” Bawendi says. “Compactness is critical for biological and a lot of other applications.”
In addition, previous efforts were unable to produce particles of uniform and predictable size, which could also be an essential property for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Moreover, Bawendi says, “We wanted to be able to manipulate these structures inside the cells with magnetic fields, but also know exactly what it is we’re moving.” All of these goals are achieved by the new nanoparticles, which can be identified with great precision by the wavelength of their fluorescent emissions.
The new method produces the combination of desired properties “in as small a package as possible,” Bawendi says — which could help pave the way for particles with other useful properties, such as the ability to bind with a specific type of bioreceptor, or another molecule of interest.
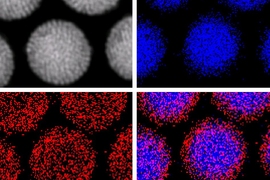
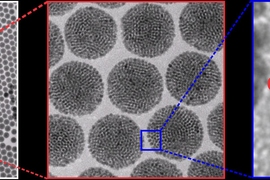
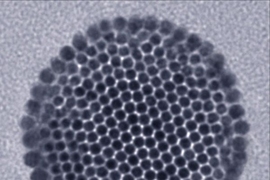
In the technique developed by Bawendi’s team, led by lead author and postdoc Ou Chen, the nanoparticles crystallize such that they self-assemble in exactly the way that leads to the most useful outcome: The magnetic particles cluster at the center, while fluorescent particles form a uniform coating around them. That puts the fluorescent molecules in the most visible location for allowing the nanoparticles to be tracked optically through a microscope.
“These are beautiful structures, they’re so clean,” Bawendi says. That uniformity arises, in part, because the starting material, fluorescent nanoparticles that Bawendi and his group have been perfecting for years, are themselves perfectly uniform in size. “You have to use very uniform material to produce such a uniform construction,” Chen says.
Initially, at least, the particles might be used to probe basic biological functions within cells, Bawendi suggests. As the work continues, later experiments may add additional materials to the particles’ coating so that they interact in specific ways with molecules or structures within the cell, either for diagnosis or treatment.
The ability to manipulate the particles with electromagnets is key to using them in biological research, Bawendi explains: The tiny particles could otherwise get lost in the jumble of molecules circulating within a cell. “Without a magnetic ‘handle,’ it’s like a needle in a haystack,” he says. “But with the magnetism, you can find it easily.”
A silica coating on the particles allows additional molecules to attach, causing the particles to bind with specific structures within the cell. “Silica makes it completely flexible; it’s a well developed material that can bind to almost anything,” Bawendi says.
For example, the coating could have a molecule that binds to a specific type of tumor cells; then, “You could use them to enhance the contrast of an MRI, so you could see the spatial macroscopic outlines of a tumor,” he says.
The next step for the team is to test the new nanoparticles in a variety of biological settings. “We’ve made the material,” Chen says. “Now we’ve got to use it, and we’re working with a number of groups around the world for a variety of applications.”
Christopher Murray, a professor of chemistry and materials science and engineering at the University of Pennsylvania who was not connected with this research, says, “This work exemplifies the power of using nanocrystals as building blocks for multiscale and multifunctional structures. We often use the term ‘artificial atoms’ in the community to describe how we are exploiting a new periodic table of fundamental building blocks to design materials, and this is a very elegant example.”
The study included researchers at MIT; Massachusetts General Hospital; Institut Curie in Paris; the Heinrich-Pette Institute and the Bernhard-Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine in Hamburg, Germany; Children’s Hospital Boston; and Cornell University. The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Army Research Office through MIT’s Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies, and the Department of Energy.