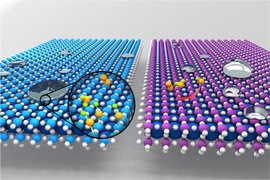
Two key physical phenomena take place at the surfaces of materials: catalysis and wetting. A catalyst enhances the rate of chemical reactions; wetting refers to how liquids spread across a surface.
Now researchers at MIT and other institutions have found that these two processes, which had been considered unrelated, are in fact closely linked. The discovery could make it easier to find new catalysts for particular applications, among other potential benefits.
“What’s really exciting is that we’ve been able to connect atomic-level interactions of water and oxides on the surface to macroscopic measurements of wetting, whether a surface is hydrophobic or hydrophilic, and connect that directly with catalytic properties,” says Yang Shao-Horn, the W.M. Keck Professor of Energy at MIT and a senior author of a paper describing the findings in the Journal of Physical Chemistry C. The research focused on a class of oxides called perovskites that are of interest for applications such as gas sensing, water purification, batteries, and fuel cells.
Since determining a surface’s wettability is “trivially easy,” says senior author Kripa Varanasi, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, that determination can now be used to predict a material’s suitability as a catalyst. Since researchers tend to specialize in either wettability or catalysis, this produces a framework for researchers in both fields to work together to advance understanding, says Varanasi, whose research focuses primarily on wettability; Shao-Horn is an expert on catalytic reactions.
“We show how wetting and catalysis, which are both surface phenomena, are related,” Varanasi says, “and how electronic structure forms a link between both.”
While both effects are important in a variety of industrial processes and have been the subject of much empirical research, “at the molecular level, we understand very little about what’s happening at the interface,” Shao-Horn says. “This is a step forward, providing a molecular-level understanding.”
“It’s primarily an experimental technique” that made the new understanding possible, explains Kelsey Stoerzinger, an MIT graduate student and the paper’s lead author. While most attempts to study such surface science use instruments requiring a vacuum, this team used a device that could study the reactions in humid air, at room temperature, and with varying degrees of water vapor present. Experiments using this system, called ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, revealed that the reactivity with water is key to the whole process, she says.
The water molecules break apart to form hydroxyl groups — an atom of oxygen bound to an atom of hydrogen — bonded to the material’s surface. These reactive compounds, in turn, are responsible for increasing the wetting properties of the surface, while simultaneously inhibiting its ability to catalyze chemical reactions. Therefore, for applications requiring high catalytic activity, the team found, a key requirement is that the surface be hydrophobic, or non-wetting.
“Ideally, this understanding helps us design new catalysts,” Stoerzinger says. If a given material “has a lower affinity for water, it has a higher affinity for catalytic activity.”
Shao-Horn notes that this is an initial finding, and that “extension of these trends to broader classes of materials and ranges of hydroxyl affinity requires further investigation.” The team has already begun further exploration of these areas. This research, she says, “opens up the space of materials and surfaces we might think about” for both catalysis and wetting.
The research team also included graduate student Wesley Hong, visiting scientist Livia Giordano, and postdocs Yueh-Lin Lee and Gisele Azimi at MIT; Ethan Crumlin and Hendrik Bluhm at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; and Michael Biegalski at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy.